Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Electric Wire for Your Next Project
When embarking on a new electrical project, one of the most critical considerations is the selection of the appropriate electric wire. The right choice can have a significant impact on the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your installation. With various types of electric wire available, each designed for specific applications, navigating the options can be overwhelming. This guide aims to provide you with essential tips to simplify the decision-making process and ensure that you choose the best electric wire for your needs.
Understanding the different characteristics and specifications of electric wire is vital for both amateur and professional electricians. Factors such as wire gauge, insulation type, and voltage rating all play crucial roles in determining the wire's suitability for a given task. Furthermore, recognizing the unique requirements of your project, including the environment and load capacity, can greatly influence your wire selection. By keeping these key aspects in mind, you will be better equipped to make informed choices that enhance the functionality and safety of your electrical work.

Understanding Different Types of Electric Wire and Their Uses
When embarking on any electrical project, understanding the different types of electric wire and their specific applications is crucial for ensuring safety and functionality. Common types of electric wire include non-metallic (NM) cable, which is suitable for indoor residential use, and armored cable (AC), known for its durability in challenging environments. Choosing the right wire not only influences the efficiency of the electrical system but also its safety.
One key tip is to always consider the wire gauge. Thicker wires (lower gauge numbers) can handle more current, which is essential for power-intensive appliances. For instance, a 12-gauge wire is appropriate for most kitchen projects, while a lighter 14-gauge wire might suffice for basic lighting fixtures. Another important factor is determining whether the wire should be rated for indoor or outdoor use. Outdoor wires require insulation that can withstand moisture and temperature fluctuations, whereas indoor wires focus on fire resistance.
Finally, understanding the insulation type is vital. Common options like THHN and THWN wires serve different environments, with THHN suitable for dry locations and THWN better for wet ones. Always check the local electrical codes to ensure compliance with safety standards. By considering these factors, you can select the right electric wire tailored to your project's specific needs and ensure a secure installation.
Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Electric Wire for Your Next Project
| Wire Type | Use Case | Ampacity | Insulation Type | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THHN | General Purpose | 30A | Nylon | Building Wire |
| Romex (NM) | Indoor Use | 20A | Thermoplastic | Residential Wiring |
| UF | Underground Use | 20A | Thermoplastic | Outdoor Wiring |
| MC Cable | Metal Clad | 30A | Metallic | Commercial Wiring |
| SOOW | Flexible Power | 50A | Rubber | Industrial Equipment |
| THWN | Wet Location | 30A | Thermoplastic | Heavy Duty Applications |
| SJOOW | Industrial Use | 60A | Thermoplastic | Motors, Equipment |
| PV Wire | Solar Applications | 20A | Cross-linked Polyethylene | Solar Panels |
| Fiber Optic Cable | Data Transmission | N/A | Varies | Internet, Communication |
| Low Voltage Wire | Low Voltage Systems | Variable | Varies | Security, Lighting |
Evaluating Electrical Ratings: Amperage, Voltage, and Temperature
When selecting the right electric wire for your project, understanding its electrical ratings is essential. The primary factors to consider are amperage, voltage, and temperature. Amperage indicates the maximum current the wire can safely conduct without overheating. Different applications will require wires rated for various amperages, so it's crucial to assess the load that the wires will need to carry. For example, residential wiring typically needs to support lower amperage compared to industrial setups, which may involve heavy machinery.
Voltage rating is another critical aspect, as it determines the maximum voltage the wire can handle safely. Choosing a wire with an insufficient voltage rating can lead to insulation breakdown and potential hazards. Assessing the voltage of your electrical system ensures that you select a wire that can manage the necessary levels without risk. Lastly, considering the temperature rating of the wire is vital, especially in environments that can fluctuate significantly or expose cables to high heat. Wires have different insulation materials, each with its temperature limits; thus, knowing the operating conditions of your project will guide you in picking the most suitable wire.
Evaluating Electrical Ratings: Amperage, Voltage, and Temperature
Assessing Insulation Materials for Your Wiring Needs
When selecting the right electric wire for your projects, one critical aspect to consider is the insulation material. Insulation plays a vital role in protecting the wire from environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and chemicals, while also ensuring safety by preventing electrical shock. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), different insulation materials can withstand varying levels of temperature and humidity, making it crucial to identify the conditions your wiring will face.
For instance, PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is commonly used for its cost-effectiveness and resilience, suitable for general applications. In contrast, silicone rubber offers higher flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures, ideal for use in harsh environments. When making your choice, it's essential to evaluate factors such as thermal performance and chemical resistance—data from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) indicates that improper insulation selection can lead to significant failures in electrical systems, underlining the importance of informed choices.
Consider these tips: First, assess the environmental conditions your wiring will encounter. For outdoor applications, investing in UV-resistant insulation can prevent deterioration. Second, evaluate the temperature rating of the insulation. Selecting wire that can handle the peak temperatures of your project ensures longevity and safety. Proper assessment of insulation materials is integral to a successful and safe wiring project, ultimately leading to robust electrical performance.
Considering Project Environment: Indoor vs Outdoor Wiring
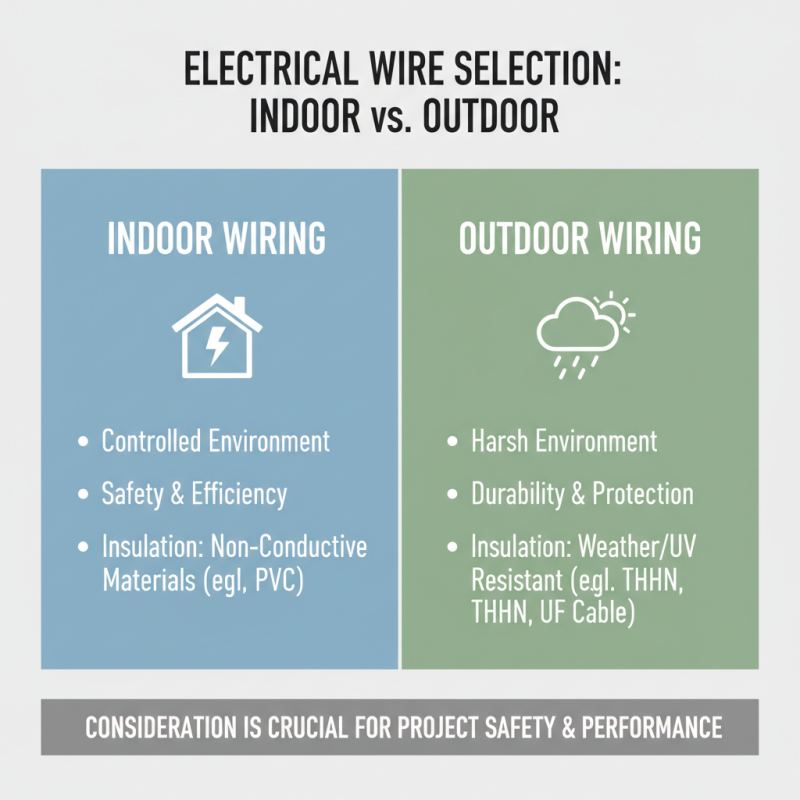
When selecting electric wire for your project, considering whether it will be used indoors or outdoors is crucial. Indoor wiring typically requires materials that are designed for safety and efficiency in a controlled environment. Wires used indoors are usually insulated with non-conductive materials that protect against accidental contact and reduce the risk of short circuits. Additionally, indoor wires may not need to withstand environmental factors like moisture or extreme temperatures, allowing for a wider variety of options that can meet the electrical demands of your project.
On the other hand, outdoor wiring presents unique challenges due to exposure to the elements. Wires intended for outdoor use must be specifically designed to resist moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. These wires often have extra insulation or protective coatings to enhance durability and prevent damage from exposure. When planning outdoor wiring, it is essential to consider the installation location, ensuring that the wire is rated for its specific setting, whether it be buried underground, mounted on a structure, or exposed to direct sunlight. Choosing the appropriate wire for the environment not only ensures a safe and reliable installation but also contributes to the longevity of your electrical system.
Safety Standards and Codes for Electric Wire Selection
When selecting electric wire for your project, adhering to safety standards and codes is paramount to ensure both safety and compliance. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines that dictate the types of conductors suitable for various applications. For instance, residential wiring typically requires the use of non-metallic sheathed cable, which must adhere to specified ampacity ratings based on the wire gauge. According to the NEC, using wire that is too small for the circuit can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards, emphasizing the need for proper selection that aligns with these codes.
Moreover, it’s essential to take into account local building codes and any additional regulations set forth by authoritative bodies. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) regularly updates safety standards, allowing professionals to stay informed about best practices. Using data from a recent electrical safety study, it was found that 50% of electrical failures were attributed to insufficient wire ratings, underscoring the relevance of industry regulations in preventing incidents. Investing in the right wire not only fortifies the safety of installations but also enhances the longevity and efficiency of electrical systems.
Related Posts
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Electric Wire: Industry Insights and Data
-

Understanding the Basics of Cable and Wire Types for Everyday Applications
-
What is Electric Wire and Why You Need to Choose the Right Type for Your Projects
-
How to Choose the Right Cable and Wire for Your Electrical Projects
-

How to Safely Perform Home Electrical Repairs: Tips and Best Practices
-

Maximizing Electrical Safety: The Essential Role of Cable Ducts in Modern Infrastructure

