How to Choose the Right Cable and Wire for Your Electrical Projects
Selecting the right cable and wire for electrical projects is a crucial step that can greatly influence the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your installations. In a world saturated with various types and specifications of cables and wires, understanding the distinctions and functions is essential for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. Whether you are wiring a new home, installing lighting fixtures, or undertaking repairs, the right choice of cable and wire ensures optimal performance and compliance with electrical codes.
When considering your options, it's important to evaluate the specific requirements of your project, including the voltage load, environmental factors, and potential future expansions. Different applications may necessitate distinct materials, gauge sizes, and insulation types, making it imperative to conduct thorough research. This guide aims to simplify the decision-making process, equipping you with the knowledge needed to select the appropriate cable and wire for your electrical undertakings, ultimately leading to successful and safe implementations.
Understanding Different Types of Cables and Wires Used in Electrical Projects

When embarking on electrical projects, understanding the different types of cables and wires is crucial for ensuring both safety and efficiency. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), there are several primary categories of cables and wires that are commonly used, including Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable (NM), Armored Cable (AC), and Various Types of Conduit and Service Entrance Wires. Each type serves specific applications; for instance, NM is mainly used for residential wiring, while AC provides a level of protection that makes it suitable for commercial installations.
The choice between these cables largely depends on factors like the environment and the electrical load they need to support. A report from the International Association of Electrical Inspectors (IAEI) highlights that incorrect selection of wire gauge can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. For instance, using a 14-gauge wire for a 20-amp circuit, when a 12-gauge is required, can compromise safety. Additionally, understanding insulation ratings is vital, as they dictate how cables respond to harsh conditions such as moisture or extreme temperatures. Selecting the correct wire type not only complies with electrical codes but also enhances the longevity and performance of your electrical systems.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Cable and Wire for Your Needs
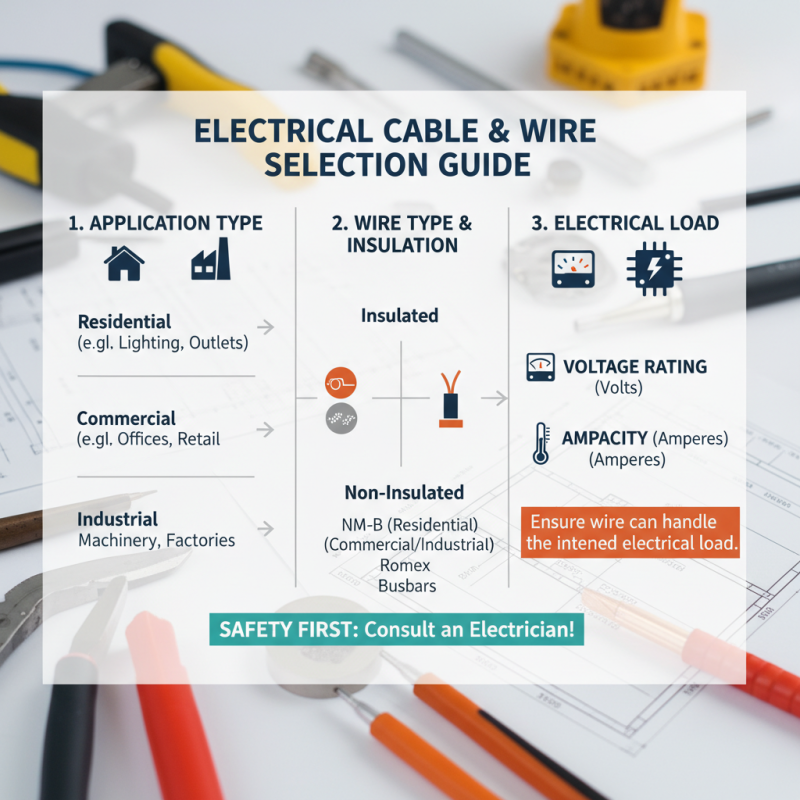
When selecting the right cable and wire for your electrical projects, there are several essential factors to consider. First, it's crucial to understand the application of the cable. Different projects may require specific types of wire, such as insulated or non-insulated, and their usage can vary widely between residential, commercial, or industrial purposes. Additionally, voltage rating and ampacity play vital roles; ensure the wire can handle the electrical load that you intend for it.
Another critical factor is the environment in which the cable will be used. Cables exposed to outdoor elements should be rated for UV resistance and moisture, while those used indoors might prioritize flexibility and low smoke emissions. It’s also important to consider the length of the run and any potential voltage drop that can occur over longer distances.
**Tips**: Always consult local electrical codes for compliance, as these regulations can dictate certain specifications. When in doubt, don’t hesitate to reach out to a professional or a knowledgeable supplier to get further insights tailored to your project needs. Choosing the correct gauge is also vital; thicker wires have lower resistance and are better suited for high-current applications.
Assessing Voltage and Current Requirements for Your Electrical Projects
When embarking on electrical projects, understanding voltage and current requirements is essential for selecting the appropriate cable and wire materials. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), residential circuits typically operate at 120V or 240V, while commercial and industrial applications often utilize higher voltages ranging from 480V up to 600V. The selection of wire sizes must adhere to these voltage levels to prevent overheating and ensure safety. For instance, a report from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) indicates that using an undersized wire can lead to a 10% drop in voltage, potentially impairing the performance of electrical equipment and increasing fire hazards.
Current requirements also play a crucial role in wire selection. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system outlines the appropriate wire sizes based on the current load they will carry, with consideration for the wire's resistance and insulation type. For example, a 12 AWG copper wire can safely carry up to 20 amps for a typical household circuit. Understanding these parameters is vital, as exceeding the ampacity can lead to heat buildup, resulting in insulation failure and electrical fires. A detailed analysis of load calculations, factoring in both continuous and non-continuous loads, is recommended for all electrical projects to ensure compliance with local safety regulations and standards.
Voltage and Current Requirements for Different Wire Gauges
This bar chart displays the maximum current capacity in amperes for various American Wire Gauge (AWG) sizes, helping you choose the appropriate wire for your electrical projects based on voltage and current requirements.
Evaluating the Environment for Cable Installation and Performance
When evaluating the environment for cable installation and performance, several critical factors come into play. First and foremost is the physical conditions where the cables will be installed. Outdoor environments expose cables to elements such as sunlight, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, which can affect their durability and functionality. For instance, UV radiation can degrade insulation materials over time, making it imperative to choose cables specifically designed for outdoor use. Similarly, wet or humid conditions necessitate the selection of moisture-resistant cables to prevent insulation breakdown and electrical failures.
Additionally, the presence of chemicals or other corrosive agents in the installation area requires careful consideration. Locations like industrial sites may have exposure to oils, solvents, or acids, which can significantly reduce the lifespan of standard cables. In such scenarios, opting for cables with enhanced chemical resistance becomes essential. Furthermore, understanding the mechanical stresses, such as bending or pulling, that the cables may experience during installation and in operation is crucial. Proper assessment of these environmental factors will ensure that the right cables are chosen, ultimately leading to safer and more reliable electrical systems.
How to Choose the Right Cable and Wire for Your Electrical Projects - Evaluating the Environment for Cable Installation and Performance
| Cable/Wire Type | Application | Environment Suitability | Temperature Rating | Maximum Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THHN Wire | General purpose wiring | Indoor, dry locations | 90°C (194°F) | 600V |
| NM-B Cable | Residential wiring | Indoor, dry locations | 90°C (194°F) | 600V |
| UF Wire | Underground service | Wet locations | 60°C (140°F) | 600V |
| XHHW Wire | Industrial wiring | Wet and dry locations | 90°C (194°F) | 600V |
| MC Cable | Commercial wiring | Indoor and outdoor | 90°C (194°F) | 600V |
Safety Standards and Regulations for Electrical Cables and Wires
When selecting electrical cables and wires for any project, understanding safety standards and regulations is crucial to ensure both reliability and compliance. In the United States, the National Electrical Code (NEC) sets the foundational standards for electrical installations, outlining requirements for wire and cable types based on their intended use, environmental conditions, and load capacity. For instance, the NEC specifies that residential wiring typically requires cables rated for 60 to 90 degrees Celsius, depending on the insulation type, contributing to the overall safety of electrical systems.
Moreover, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides global standards that help harmonize safety protocols across different countries. According to recent industry reports, adherence to these standards significantly reduces the incidence of electrical fires, which have been reported to cause over
$1.3 billion in property damage annually in the U.S. alone. By following these regulations, professionals can mitigate risks associated with overheating, short circuits, and electrical failures, fostering safer environments for both residential and commercial settings. Thus, grounding decisions in established safety standards not only enhances the integrity of electrical installations but also protects end users from potential hazards.
Related Posts
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Electric Wire: Industry Insights and Data
-

Revolutionize Your Workspace: Unleashing the Power of Innovative Cable Holders
-

Maximizing Efficiency: How Electric Cable Ducts Improve Cable Management and Reduce Risks in Modern Infrastructure
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Duct Cable for Your Networking Needs
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Cable Cover for Your Home and Office
-

Understanding the Importance of Duct Cable in Modern Communication Systems

